The Impact of Exotic Species on Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Exotic Species
As globalization continues to expand, the influence of species is no longer confined to their natural habitats. When species reside or thrive outside their original environments, they are classified as exotic or invasive species. These species pose significant threats to biodiversity, which refers to the variety of life forms within a specific area. They disrupt the structure and functions of natural ecosystems, particularly by altering seed dispersal mechanisms. Notably, around 90% of plants in tropical areas rely on animals for seed dispersal, while this figure is approximately 60% in non-tropical regions.
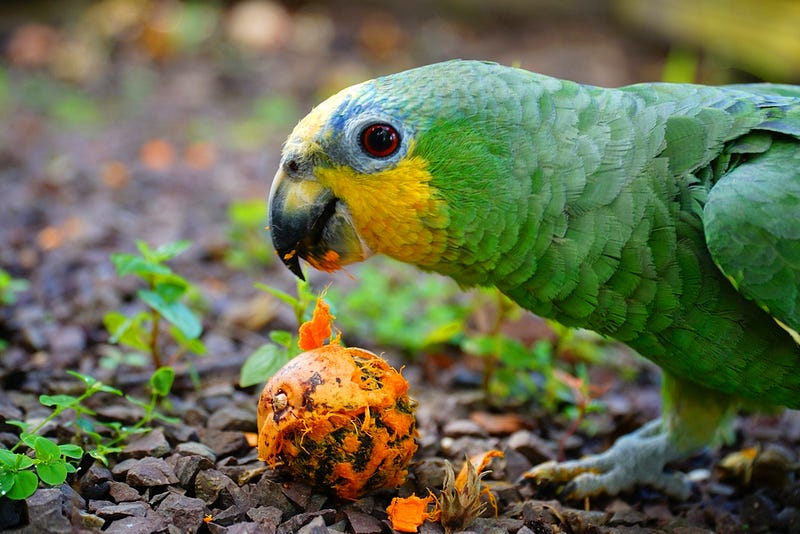

Chapter 2: The Effects of Exotic Species on Native Flora
One primary impact of exotic species is their influence on native plant populations. For instance, the European rabbit, while effective at dispersing seeds, also promotes the growth of invasive plants and consumes native tree seedlings. Similarly, parrots can facilitate the spread of both native and invasive plants by carrying seeds or excreting them after consuming fruits. Other exotic birds may also aid in seed dispersal, but their efficiency is generally lower, resulting in fewer seeds germinating or being damaged before dispersal.
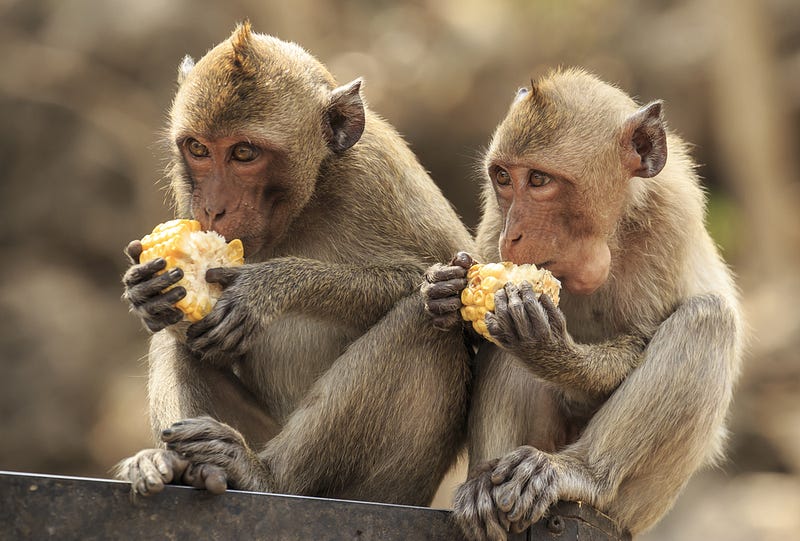
Additionally, the long-tailed macaque exemplifies another way exotic species can harm native flora. While they spread seeds, they often discard immature native fruits in favor of exotic ones, leading to a decline in the native seed population.
Section 2.1: Disruption of Mutual Dependencies
Exotic species also disrupt the mutual dependencies that exist between plants and animals. For example, plants provide fruits that serve as food for animals, who in return, help disperse the plants' seeds. The introduction of exotic species can upset this balance, as these plants may compete with native species for animal attention, causing a decrease in visits to native plants.
Moreover, the introduction of exotic animals can directly impact native fauna. If they hunt native species, those animals may either relocate or perish, further diminishing seed dispersal in their original habitats. The loss of these critical relationships can lead to significant indirect consequences, including the potential extinction of native plant species, which in turn affects the ecosystem's overall health.

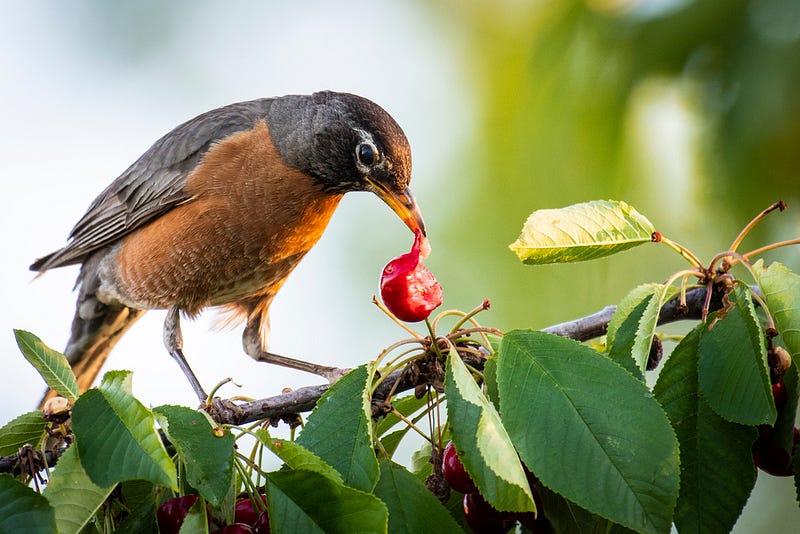
Section 2.2: Seed Quality Impairment
Another significant concern is how exotic species affect seed quality. Some exotic species may consume or damage seeds, preventing them from germinating. Additionally, certain species may remove essential parts of seeds that attract ants, which typically assist in dispersing them. Without these critical components, seeds lose their chance of being spread effectively.

Chapter 3: The Role of Exotic Species in Habitat Restoration
Interestingly, some exotic species can inadvertently support habitat restoration. For instance, fennel attracts specific bird species that help disperse seeds, promoting growth in the area. Similarly, guava trees contribute to seed dispersal through their prolific seed rain, fostering the growth of native plants in subsequent generations.

Although these effects may appear beneficial in the short term, the potential for negative indirect consequences must be considered. A reduction in plant diversity can make habitats more vulnerable to diseases, highlighting the need for caution.
Conclusion: Addressing the Impact of Exotic Species
In summary, exotic species significantly impact ecosystems by altering native plant populations, disrupting mutual dependencies, and affecting seed quality, while also playing a complex role in habitat restoration. While their influence may seem positive in specific contexts, it is crucial to recognize the broader implications of these changes.
How Can We Mitigate These Effects?
To counteract the detrimental impacts of exotic species, individuals can take several practical steps:
- Avoid bringing seeds when traveling.
- Refrain from adopting exotic animals as pets.
- Plant native species in personal gardens.
- Verify the native status of plants in gardens.
- Avoid feeding exotic animals.
What actions can you implement in your daily life to help combat these issues? Feel free to share your ideas in the comments to inspire others.
Credit
This article is grounded in the research by Cordero, S., Gálvez, F., & Fontúrbel, F. E. (2023). "Ecological Impacts of Exotic Species on Native Seed Dispersal Systems: A Systematic Review." Plants, 12(2), 261.
The first video titled "How invasive species affect Biodiversity" explores the intricate relationships between invasive species and biodiversity, shedding light on their ecological consequences.
The second video, "Invasive plants and their effect on native ecosystems | Jacob Llodra | TEDxYouth@GDRHS," delves into the impact of invasive plants on local ecosystems, emphasizing the need for awareness and action.