Revolutionizing Physics: Discoveries That Challenge Our Understanding
Written on
Chapter 1: Recent Breakthroughs in Physics
In recent weeks, the scientific community has witnessed both shocking and remarkable developments in the realm of fundamental physics.
This paragraph will result in an indented block of text, typically used for quoting other text.
Section 1.1: Enhancing Precision in Measurements
After years of dedicated research, scientists at the renowned Fermilab in the United States have successfully improved the precision of measuring the muon's anomalous magnetic moment. This advancement has led to a compelling conclusion: the predictions made by the Standard Model of particle physics do not align with the experimental findings (assuming the theoretical calculations hold true). Though the limitations of the Standard Model have been acknowledged for years, we are now confronted with clear discrepancies for the first time. History teaches us that such contradictions often fuel progress, highlighting a path forward in scientific inquiry.

Section 1.2: A Groundbreaking Study on Stellar Motion
The most striking revelation comes from a paper by Korean researcher Kyu-Hyun Chae, published in the esteemed "Astrophysical Journal." This research investigates the motion of stars within expansive binary systems, where the two stars are separated by distances that can range from tens to thousands of astronomical units.

Why are these findings so significant? Almost a century ago, initial indications suggested anomalies in the motion of stars within galaxies. While those near the galactic center conformed to gravitational predictions, distant stars began to show discrepancies. These deviations became particularly pronounced when the stars' motion experienced low acceleration.
This critical acceleration is approximately one-ten-billionth of Earth's gravity, or a millionth of the acceleration at which Earth orbits the Sun. Astrophysicists refer to this phenomenon as the "flattening" of stellar rotational motion. Notably, this critical acceleration closely aligns with the rate of the Universe's expansion—a curious coincidence that may hint at deeper underlying principles.

Section 1.3: The Dark Matter Hypothesis
Gravity is inherently linked to mass, leading to the simplest explanation for the peculiar stellar movements: the existence of dark matter—an invisible form of matter that influences gravitational interactions without emitting light. Despite rigorous investigations by particle physicists, no evidence of dark particles has been discovered, nor has a widely accepted theoretical framework emerged.
With experimental results at hand, scientists can ascertain the level of confidence in their findings. A confidence level of 1σ indicates an 84.1% probability that the result is accurate, while 2σ corresponds to a 97.7% chance. In particle physics, a confidence level of at least 5σ (99.9999426697% certainty) is typically required for a measurement to be deemed reliable.
An alternative explanation posits that at very low accelerations, gravitational theory may require modifications. This idea was proposed four decades ago by Israeli physicist Mordechai Milgrom through his Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) theory, suggesting a universal acceleration scale below which traditional gravitational predictions fail.
Chapter 2: Investigating Stellar Systems
To discern which explanation holds true, researchers can examine systems where dark matter's influence is negligible, particularly where accelerations hover around the critical threshold. If deviations from Newtonian predictions emerge in these environments, it would strongly imply that the current understanding of physics needs revision.
The European space telescope Gaia has provided invaluable observational data, uncovering over a million binary systems within a 1000 parsec radius. However, only a fraction of these systems is suitable for low-acceleration studies. Kyu-Hyun Chae's analysis successfully narrowed the list to approximately four thousand viable systems.
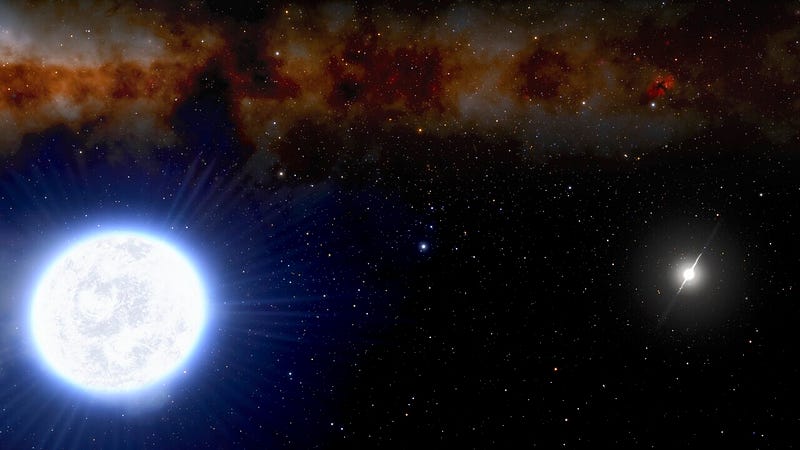

The analysis of these binary systems yielded compelling evidence: within a confidence interval surpassing 5σ, significant deviations from gravitational theory were observed as star motion's acceleration fell below the critical threshold. With no visible dark matter explanation for this effect, the findings strongly suggest that gravitational theory may need to be adjusted.
What an intriguing paradox! If Kyu-Hyun Chae's conclusions are validated, physicists may be compelled to rethink the very foundations of gravitational theory, which also encompasses the nature of time and space.
For decades, fundamental physics has sought out new challenges at extreme energy levels, colliding elementary particles in hopes of unveiling nature's deepest secrets. Paradoxically, the hidden treasures may lie within phenomena occurring at minimal accelerations, and discovering them could herald a new scientific revolution with unforeseen implications.
This video titled "Sparking the Scientific Revolution | Modern World History 16 of 30 | Study Hall" explores the pivotal changes in scientific thought that have shaped modern physics.
In "How the Scientific Revolution Changed the World (#ProjectRevolution)," the discussion focuses on the transformative impacts of scientific advancements on society and knowledge.
Attention All Readers!
As content creators on Medium.com, we often receive minimal compensation for our efforts. If you appreciate my articles, please consider supporting me on my "Buy Me a Coffee" page. Your contributions can significantly aid in my pursuit of creating quality content. Thank you for your support!

